As reported in our 2017 LNG Demand: China and Europe drive growth blog, 2017 saw a record year for global LNG trade, with 290mt changing hands over the course of the year. This ca. 10% (27mt) year-on-year increase from 2016 figures was driven primarily by demand growth from China, South Korea and a return to growth in Europe.
Strong demand growth continues
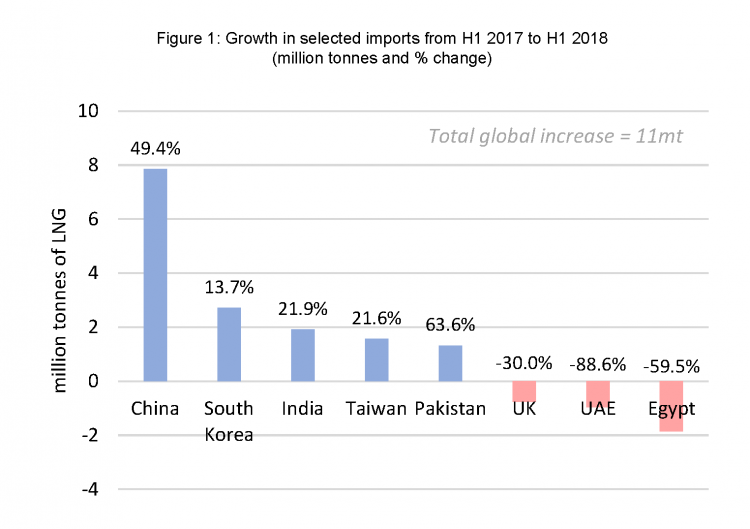
This growth has continued into H1 2018 with a ca. 8% (11mt) increase compared to the same period in 2017. Chinese demand has continued to surge on the back of an aggressive coal to gas switching policy, with imports up by ca. 49% (8mt) in H1 2018 (c.f. H1 2017). This fuel switching policy has enjoyed considerable success –coal consumption in Beijing has plunged from ca. 20mt in 2013 to ca. 5mt in 2017, while PM2.5 (an air pollutant indicator) in Beijing has also decreased, falling by 35% over the past five years. South Korea has seen a continued increase in imports with a ca. 14% (3mt) year-on-year increase, also buoyed by supportive policy. In addition to supportive policy, North Asia experienced a particularly cold winter, with temperatures almost 1°C below average.
Other sizeable contributors to the H1 2018 growth include India (LNG price competitiveness and new supply contracts), Taiwan (supportive policy) and Pakistan (shortage of gas and current competitive price of LNG) - see Figure 1 below.
Source: Gas Strategies and Thomson Reuters
However, several countries have seen LNG imports decrease in the first half of this year due to a range of factors:
- Pricing: the increased Asian demand put upwards pressure on pricing, attracting more cargoes from the UK and European markets to the Asian market
- Political tensions: the political fallout between the UAE and Qatar has brought a halt to LNG trade between the countries, which has had a substantial impact on the UAE’s LNG imports
- Zohr production: the giant Zohr gas field has boosted indigenous production in Egypt and will contribute to the continued reduction in LNG imports
- Nuclear restarts: Japanese LNG imports have fallen by ca. 2% (0.7mt) in H1 2018, due to the restart of three nuclear reactors between March and May this year
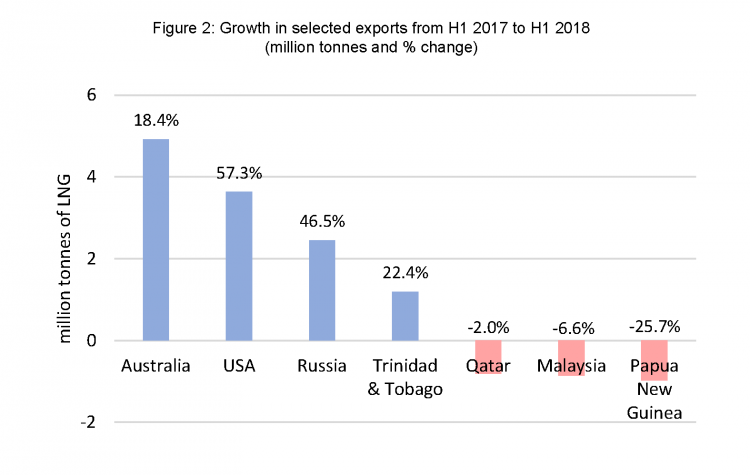
Australian and US LNG wave continues
The strong net increase in demand was met largely with supply from new facilities, including the Wheatstone project in Australia, the Cove Point facility in the US and the Yamal project in Russia. Atlantic LNG in Trinidad and Tobago also increased production thanks to two new projects (Trinidad Onshore Compression and Juniper projects, completed in 2017). Offsetting these supply increases were temporary reductions in supply from Papua New Guinea (6-week production outage due to late February earthquake), Malaysia (gas pipeline disruption and separate technical problems) and Qatar (maintenance) - see Figure 2 below.
Source: Gas Strategies and Thomson Reuters
Demand hinges on Asia
Should this 8% growth trend continue for the remainder of the year, annual global LNG trade would reach 313mt. Asia is expected to continue to spearhead LNG demand growth, supported by pro-gas policy in China, South Korea and Taiwan. India and Pakistan are also projected to continue their growth to meet domestic gas demand, supported by competitive LNG pricing and a potential market loosening as we head towards 2019.
However, the level of Asian demand growth in the short term is by no means guaranteed to maintain its steep trajectory, as restarts of several Japanese and South Korean nuclear facilities are expected to have a negative impact on LNG demand. The Yuan's sharp decline versus the dollar could also slightly hinder LNG demand in China, making US dollar denominated LNG costlier for Chinese buyers.
Demand in Europe is projected to be unpredictable for the remainder of the year and into 2019, as it is likely to act as a market buffer for global supply and demand imbalances. A watchpoint in Europe will be carbon pricing, with the EU ETS rising by ca. 119% so far since January 1 2018. Middle Eastern demand is expected to maintain its decline, continuing to be impacted by Zohr development and production.
A market in balance?
A potential ‘supply glut’ had been mooted in recent years, with question marks over the ability of the market to absorb the swath of new Australian, US and Russian supply entering the markets from the mid-2010s onwards. This glut has so far failed to materialise, primarily due to the rapid Chinese demand growth and delays to several LNG projects.
As additional projects are due to come online later this year and in 2019, such as the Ichthys and Prelude projects in Australia, and Yamal T2 in Russia, some question marks remain as to whether demand can maintain its current proportional rise with supply. However, current indicators continue to point to strong demand, with the probability of the ’glut’ ever eventuating now greatly diminished.
If you would like more information about how Gas Strategies can help your business with Consulting services across the value chain or provide industry insight with regular news, features and analysis through Information Services or help with people development through Training Services, please contact us directly.